More frequent and heavier rainfall has increased the risk of flooding and the dangers and damage that come with it. This forces cities to think about climate change adaptation and mitigation. Since 2009 the Danish Government has provided municipalities with data about climate change and flooding and since 2014 every Danish municipality has developed a climate change adaptation plan. There is a multitude of options for detaining, draining and redirecting rainwater and it is not immediately clear which solution is best. Damage costs from flooding differ from area to area and thus different protection measures are required. Municipalities want to make the right decision and protect areas in accordance with their values.
Solution
In 2014 the Danish Environmental Protection Agency began development of a software tool called PLASK, which stands for Project on Local Analysis of the Social-Economics of Climate Adaptation. The tool helps municipalities compare the socio-economic impact and economic effects of different protection measures and determine the optimal protection level.
First, the tool calculates the cost of damages in the project area in case of flooding for different land use types. Historical values of insurance payments are combined with taxation values.
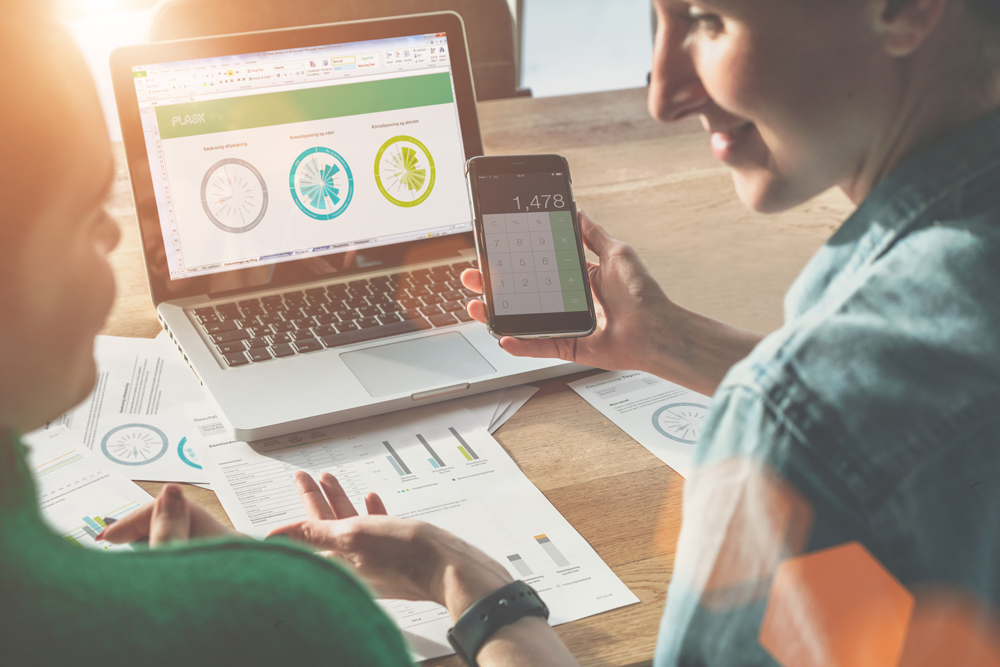

The tool also incorporates the long-term and short-term investment and maintenance costs of the different flood-prevention solutions. Using this data, the tool executes a cost-benefit analysis to calculate the optimal level of climate adaptation to protect the area and discounts the values over the lifespan of the project to get a net present value of the different solutions/projects.
This allows users to more quickly and accurately compare climate adaptation solutions.
Second, the tool calculates the distribution of benefits and effects other than economic value. The tool shows different options for achieving the same level of protection against flooding and outlines the effects of each solution in terms of, for example, biodiversity, energy-efficiency and public health.
Outcome
The PLASK tool is used to compare different climate change protection projects from both a cost-efficiency and welfare-economic perspective. By taking into account many different parameters it has helped planners to think about climate change adaptation in a more holistic way and make better decisions.
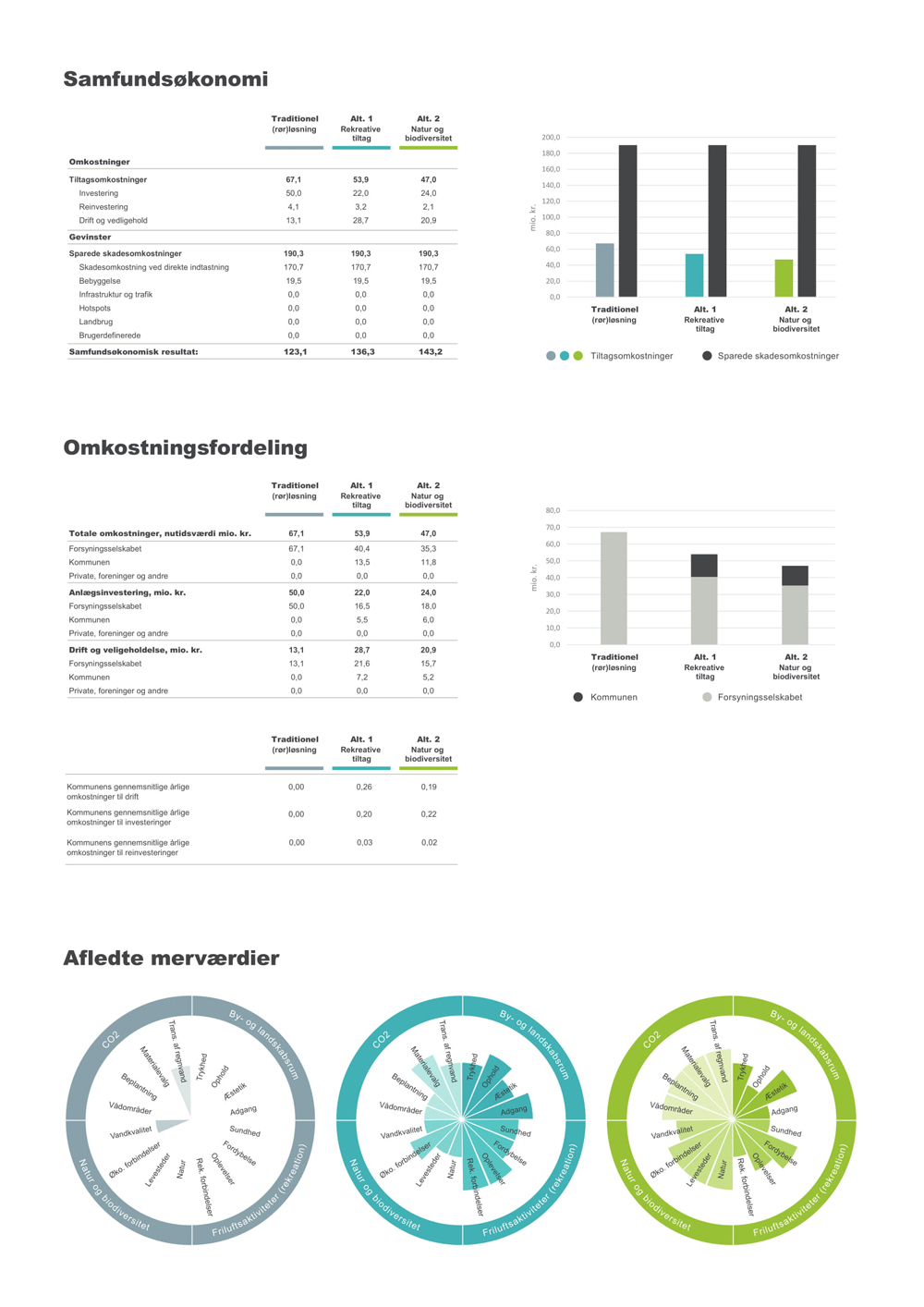
In the municipality of Lolland in Denmark local authorities have used PLASK to determine that the most cost-effective flood-prevention solution is a lake to receive rainwater during peaks of rainfall. This solution is substantially cheaper than the conventional underground drainage system.
Users have added their own parameters and functions or used the tool to crosscheck values. The tool was updated in 2017 and is being tested on four projects in Denmark under the Rain and Cities partnership. The results will become available in 2019.
Potentials
Thinking about climate change adaptation is evolving and so is the tool. New methods are being devised and old methods for adaptation are becoming more common and thus cheaper.
By applying local data and parameters, the tool can be used in any context to make better financial and welfare-economic decisions regarding climate change adaptation.
Learn more
PLASK – Projekt om Lokale Analyser af Samfundsøkonomi i Klimatilpasning