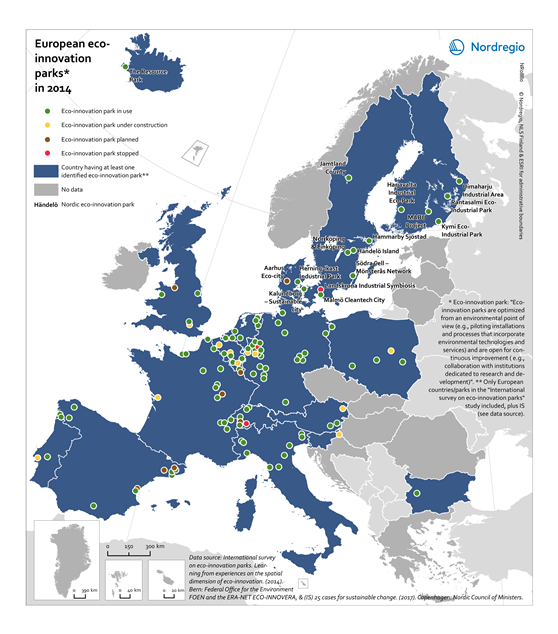
This map shows the location of the European eco-innovation parks in the states of the European Union (EU) and Iceland in 2014. The eco-innovation parks are eco-industrial parks and eco-innovative areas combining residential and industrial activities.
The establishment of eco-industrial parks is one way to promote eco-innovation, resource efficiency and the circular economy. They create new and innovative business opportunities and improve ecosystems.
The blue colour indicates the EU-member states having at least one identified eco-innovation park in 2014. The circles indicate the location and the type of the eco-innovation parks (green, in use; yellow, under construction; brown, planned; red, stopped). The grey colour indicates no data.
A clear spatial concentration of eco-innovation parks can be observed in the Ruhr area and around Leipzig (Germany), in southern Belgium, south-western and northern Netherlands, western Switzerland, along the “arch” stretching from Turin via Pisa to Udine in North-East Italy, around Barcelona as well as around some national borders in the industrialised parts of north-West Europe namely Germany-Netherlands-Belgium-France and Switzerland.
Eco-innovation parks differ in many respects, for instance regarding energy and material flows (e.g. waste heat, steam, power; wood chips, bark, ash, pulping chemicals), number and size of companies involved and jobs created, public sector involvement and finally, in terms of (the drivers behind) their evolution. The latter means that some parks evolved and expanded around a few economic activities and companies (e.g. saw mills) to include further activities (e.g. pulp mills, power plants etc.), while others were intentionally planned and put into operation.