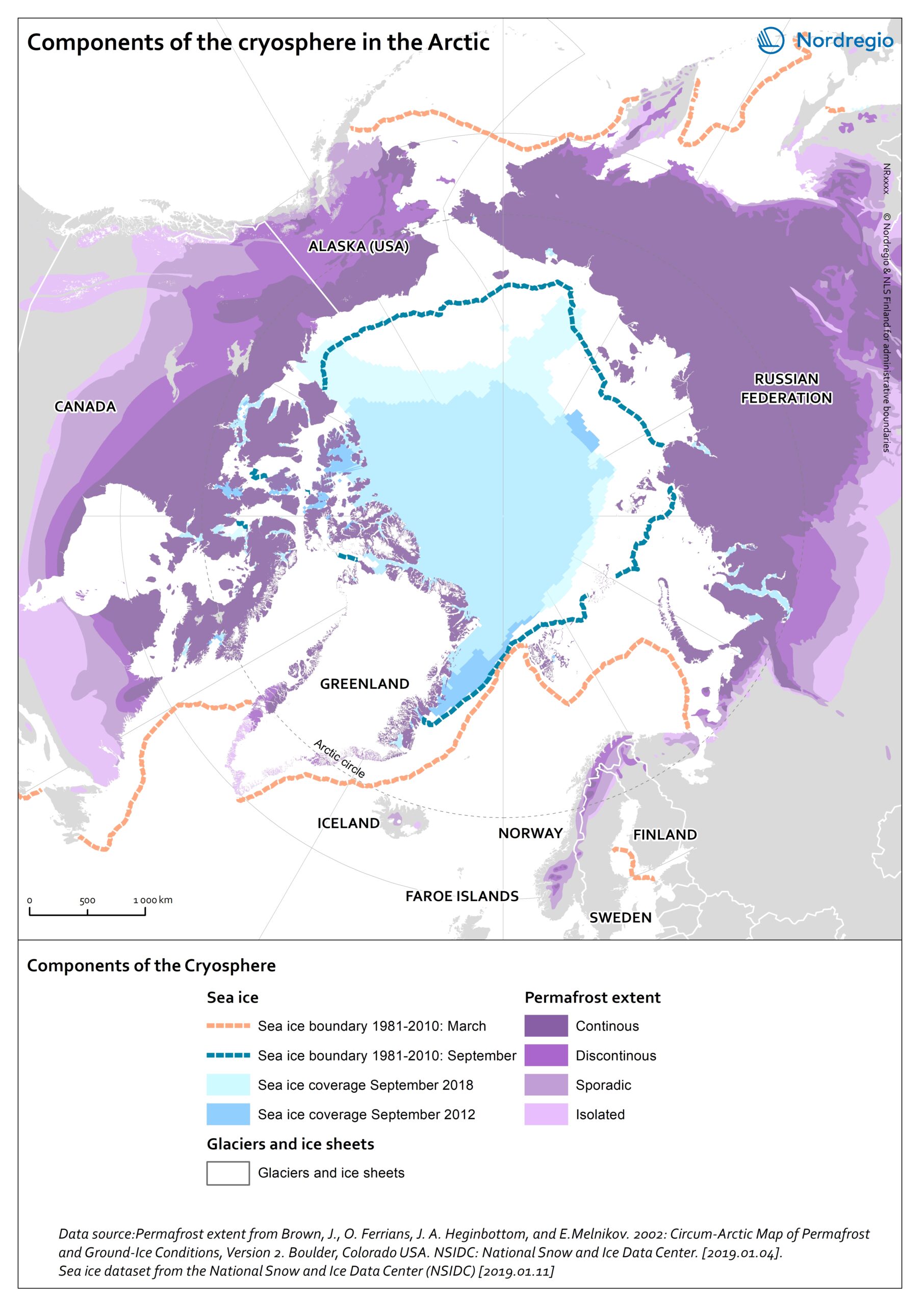
This map shows the main components of the cryosphere in the Arctic: sea-ice, permafrost, ice-sheets, and glaciers.
Sea-ice covers most of the Arctic Ocean during winter. The sea-ice extent reaches its maximum in March, when it covers approximately 14-16 million km2. Since 1979, the Arctic ice extent in winter has decreased by 3% per decade relative to the 1981-2010 average, and this trend accelerates. Similarly, ice-sheets and glaciers, which cover globally over 15 million km2 are melting. In the Arctic, the main ice-sheet is the Greenlandic ice sheet.
Most of the land surface in the Arctic is underlay by permafrost, ground that is at or below 0°C for at least 2 consecutive years. The purple tones on the map indicates the extent of the northern circumpolar permafrost. Permafrost can occur as continuous (dark purple, 90-100% coverage), discontinuous (purple, 50-90% coverage), sporadic (light purple, 10-50%), or isolated patches (magenta, 0-10% coverage). Permafrost is thawing due to increased air temperatures and precipitations in the Arctic. Permafrost temperature increased by 0.29 ± 0.12°C between 2007 and 2016.