To secure better access to general practitioners for the rural population, the region of Västerbotten has developed the concept of virtual health
rooms (VHRs). These VHRs are unstaffed, which means that they have no regular health personnel in situ. They are equipped with distance-spanning
technology, which means that patients can go there to take consultations from a practitioner online, conducting health checks such as measuring
blood pressure or heart rate.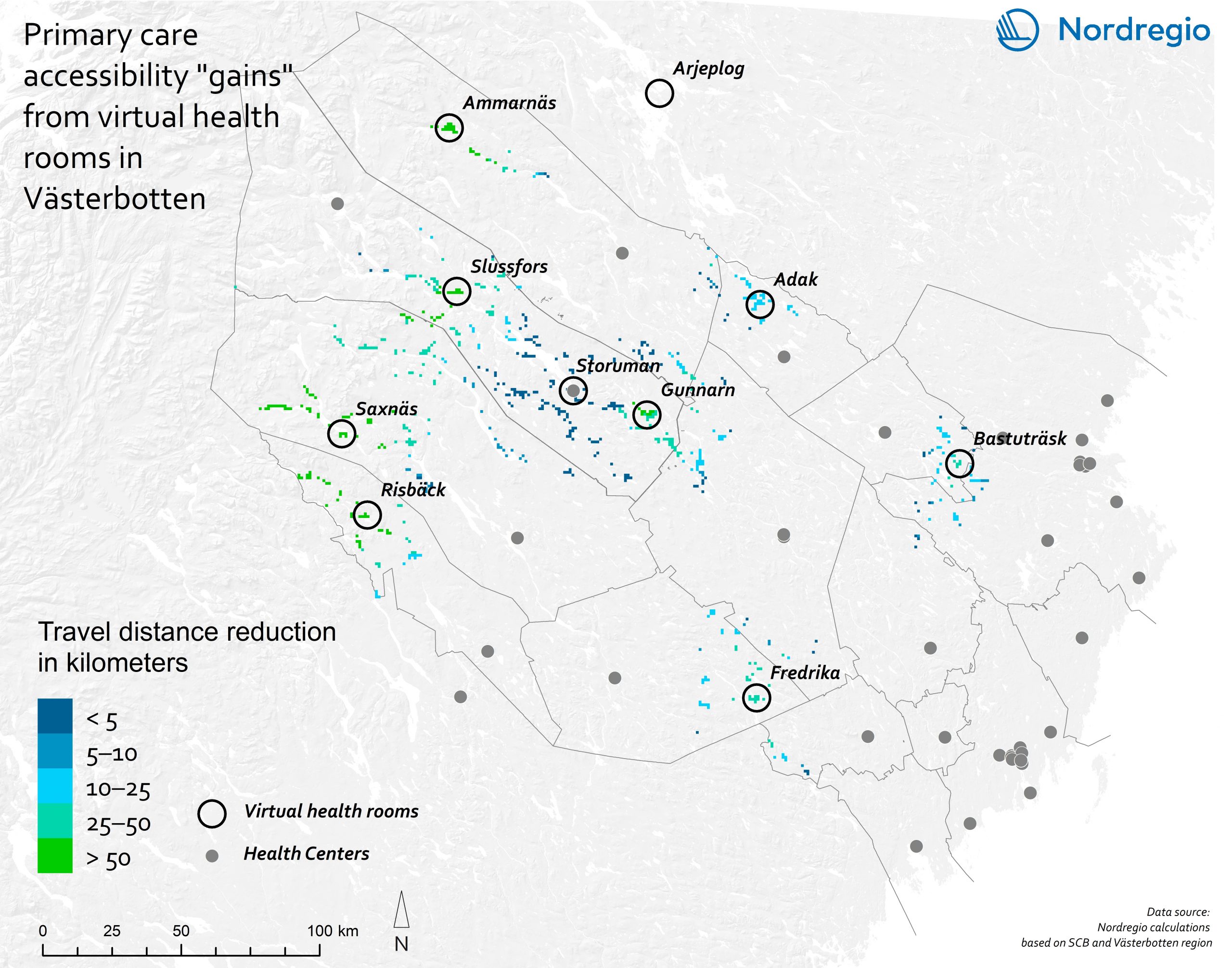
The coloured patches on the map show those populated areas in Västerbotten where inhabitants can expect a reduction of travel distance to primary health care through the implementation of VHRs. The coloured patches are populated areas in Västerbotten (by 1000*1000m grid) with improved accessibility of health care resulting from the implementation of virtual health rooms. The colour indicates the total distance reduced.
Distance is measured as being via the road network.
The average distance to the closest primary health care facility (health centre or virtual health room) is 6 km for the overall population in Västerbotten. The implementation of VHRs means that around 3.5% of the 270,000 inhabitants of Västerbotten experience increased accessibility to
a primary health care service. The travel distance for this portion of the population has been cut by almost 50%, from 42 km per person to 23 km per person. Patients may also use virtual health rooms to conduct teleconsultations with health professionals at specialised hospitals, which creates even greater potential from an accessibility standpoint.
Related Staff
Related Research Projects
Related Maps
- Accessibility of highly specialised care in Nordjylland
- Accessibility of highly specialised care in Västerbotten
- Accessibility of in-patient care in Eastern health region
- Accessibility of in-patient care in Nordjylland
- Accessibility of in-patient care in Sogn og Fjordane
- Accessibility of in-patient care in Västerbotten
- Accessibility of out-patient drop-in care during non-office hours and in-patient care in South Karelia
- Accessibility of out-patient drop-in care during non-office hours in Sogn og Fjordane
- Accessibility of out-patient drop-in care during office hours in Sogn og Fjordane
- Accessibility of out-patient drop-in care during office hours in South Karelia
- Accessibility of out-patient drop-in care in Eastern health region
- Accessibility of out-patient drop-in care in Västerbotten
- Accessibility of primary care in Eastern health region
- Accessibility of primary care in South Karelia
- Accessibility of primary care in Västerbotten
- Accessibility to out-patient drop-in care during non-office hours in Nordjylland
- Accessibility to out-patient drop-in care during office hours in Nordjylland
- Accessibility to primary care in Nordjylland
- Accessibility to primary care in Sogn og Fjordane